Convert PySpark DataFrame Column from String to Int Type (5 Examples)
In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to convert a PySpark DataFrame column from String to Integer Type in the Python programming language.
The table of content is structured as follows:
- Introduction
- Creating Example Data
- Example 1: Using int Keyword
- Example 2: Using IntegerType() Method
- Example 3: Using select() Function
- Example 4: Using selectExpr() Method
- Example 5: Using SQL
- Video, Further Resources & Summary
Fasten your seatbelt so we can start!
Introduction
PySpark is an open-source software that is used to store and process data by using the Python Programming language.
We can generate a PySpark object by using a Spark session and specify the app name by using the getorcreate() method.
SparkSession.builder.appName(app_name).getOrCreate() |
SparkSession.builder.appName(app_name).getOrCreate()
After the data set with a list of dictionaries is created, we have to pass the data to the createDataFrame() method. Now we have created a PySpark DataFrame.
spark.createDataFrame(data) |
spark.createDataFrame(data)
After that we can display the DataFrame by using the show() method as you can see below:
dataframe.show() |
dataframe.show()
Now we are ready for creating our example data.
Creating Example Data
In this example, we are going to create a DataFrame from a list of dictionaries with eight rows and three columns, containing fruits and city details. To display the DataFrame we are using the show() method:
# import the pyspark module import pyspark # import the sparksession from pyspark.sql module from pyspark.sql import SparkSession # creating sparksession and then give the app name spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('statistics_globe').getOrCreate() #create a dictionary with 3 pairs with 8 values each #inside a list data = [{'fruit': 'apple', 'cost': '67.89', 'city': 'patna'}, {'fruit': 'mango', 'cost': '87.67', 'city': 'delhi'}, {'fruit': 'apple', 'cost': '64.76', 'city': 'harayana'}, {'fruit': 'banana', 'cost': '87.00', 'city': 'hyderabad'}, {'fruit': 'guava', 'cost': '69.56', 'city': 'delhi'}, {'fruit': 'mango', 'cost': '234.67', 'city': 'patna'}, {'fruit': 'apple', 'cost': '143.00', 'city': 'delhi'}, {'fruit': 'mango', 'cost': '49.0', 'city': 'banglore'}] # creating a dataframe from the given list of dictionary dataframe = spark.createDataFrame(data) # display the final dataframe dataframe.show() |
# import the pyspark module import pyspark # import the sparksession from pyspark.sql module from pyspark.sql import SparkSession # creating sparksession and then give the app name spark = SparkSession.builder.appName('statistics_globe').getOrCreate() #create a dictionary with 3 pairs with 8 values each #inside a list data = [{'fruit': 'apple', 'cost': '67.89', 'city': 'patna'}, {'fruit': 'mango', 'cost': '87.67', 'city': 'delhi'}, {'fruit': 'apple', 'cost': '64.76', 'city': 'harayana'}, {'fruit': 'banana', 'cost': '87.00', 'city': 'hyderabad'}, {'fruit': 'guava', 'cost': '69.56', 'city': 'delhi'}, {'fruit': 'mango', 'cost': '234.67', 'city': 'patna'}, {'fruit': 'apple', 'cost': '143.00', 'city': 'delhi'}, {'fruit': 'mango', 'cost': '49.0', 'city': 'banglore'}] # creating a dataframe from the given list of dictionary dataframe = spark.createDataFrame(data) # display the final dataframe dataframe.show()
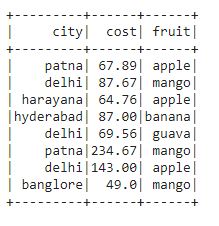
The previously shown table includes our example DataFrame. As you can see, it contains three columns that are called city, cost and fruit with string data types.
Let’s convert the string type of the cost column to an integer data type.
Example 1: Using int Keyword
This example uses the int keyword with the cast() function and converts the string type into int.
We can display the DataFrame columns by using the printSchema() method.
dataframe.withColumn("column_name",dataframe.cost.cast('int')).printSchema() |
dataframe.withColumn("column_name",dataframe.cost.cast('int')).printSchema()
In this example, we are converting the cost column in our DataFrame from string type to int:
#convert the city column data type into integer using int keyword dataframe.withColumn("cost",dataframe.cost.cast('int')).printSchema() |
#convert the city column data type into integer using int keyword dataframe.withColumn("cost",dataframe.cost.cast('int')).printSchema()

Example 2: Using IntegerType() Method
This example uses the IntegerType() method imported from pyspark.sql.functions with the cast() function and converts the string type into integer.
After that, we can display the DataFrame columns by using the printSchema() method:
#import IntegerType method from pyspark.sql.types import IntegerType #convert string to Integer for cost column dataframe.withColumn("cost",dataframe.cost.cast(IntegerType())).printSchema() |
#import IntegerType method from pyspark.sql.types import IntegerType #convert string to Integer for cost column dataframe.withColumn("cost",dataframe.cost.cast(IntegerType())).printSchema()

Example 3: Using select() Function
This example uses the select() function with the col() method imported from pyspark.sql.functions by cast() function and converts the string type into integer.
After that, we can display the DataFrame columns by using the printSchema() method:
dataframe.select(col("column_name").cast('int').alias("column_name")).printSchema() |
dataframe.select(col("column_name").cast('int').alias("column_name")).printSchema()
In this example, we are converting the cost column in DataFrame from string type to integer:
#import col from pyspark.sql.functions import col # Use select function to convert cost column data type to Integer dataframe.select(col("cost").cast('int').alias("cost")).printSchema() |
#import col from pyspark.sql.functions import col # Use select function to convert cost column data type to Integer dataframe.select(col("cost").cast('int').alias("cost")).printSchema()
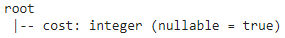
Example 4: Using selectExpr() Method
This example uses the selectExpr() function with a keyword and converts the string type into integer.
dataframe.selectExpr("column_name","cast(column_name as int) column_name") |
dataframe.selectExpr("column_name","cast(column_name as int) column_name")
In this example, we are converting the cost column in our DataFrame from string type to integer.
# use select expression to convert string to Integer type of cost column dataframe.selectExpr("city","cast(cost as int) cost") |
# use select expression to convert string to Integer type of cost column dataframe.selectExpr("city","cast(cost as int) cost")
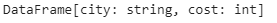
Example 5: Using SQL
This example uses a SQL query to convert a string to an integer type with:
spark.sql("SELECT INT(column_name) as column_name from view_name") |
spark.sql("SELECT INT(column_name) as column_name from view_name")
In this example we are converting the cost column in our DataFrame from string type to integer:
#create view dataframe.createOrReplaceTempView("data") # use sql function to convert string to integer data type of cost column spark.sql("SELECT INT(cost) as cost from data") |
#create view dataframe.createOrReplaceTempView("data") # use sql function to convert string to integer data type of cost column spark.sql("SELECT INT(cost) as cost from data")
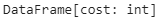
Video, Further Resources & Summary
Do you need more explanations on how to convert a PySpark DataFrame column from string to int data type, then you may have a look at the following YouTube video of the DecisionForest YouTube channel.
By loading the video, you agree to YouTube’s privacy policy.
Learn more
Furthermore, you may have a look at some other tutorials on the Data Hacks website:
- Add New Column to PySpark DataFrame in Python
- Change Column Names of PySpark DataFrame in Python
- Concatenate Two & Multiple PySpark DataFrames
- Convert PySpark DataFrame Column from String to Double Type
- Display PySpark DataFrame in Table Format
- Export PySpark DataFrame as CSV
- Filter PySpark DataFrame Column with None Value in Python
- groupBy & Sort PySpark DataFrame in Descending Order
- Import PySpark in Python Shell
- Python Programming Tutorials
Summary: This post has illustrated how to switch from string to int type in a PySpark DataFrame in the Python programming language. In case you have any additional questions, you may leave a comment below.
This article was written in collaboration with Gottumukkala Sravan Kumar. You may find more information about Gottumukkala Sravan Kumar and his other articles on his profile page.
